Active Directory Group Policies allow you to centrally apply the same settings for multiple computers and/or domain users and greatly simplify configuration management in an AD domain environment. The Group Policy Management Console ( GPMC.msc ) is the main tool for managing Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Active Directory.
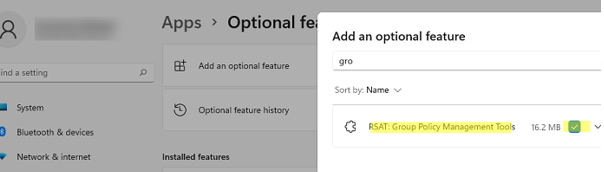
In Windows 10 and 11, the GPMC console comes as part of RSAT, a feature you can install through the Settings panel. Go to Settings -> Apps -> Optional Features -> Add an optional feature -> select RSAT: Group Policy Management Tools and click Install.

You can also install the Group Policy Management Console on Windows 10 and 11 via PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
DISM.exe /Online /add-capability /CapabilityName:Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Please note that modern versions of Windows 10 and 11 require your computer to be connected to the internet in order to install the RSAT management tools. See the article at the link for more information on installing RSAT on Windows.
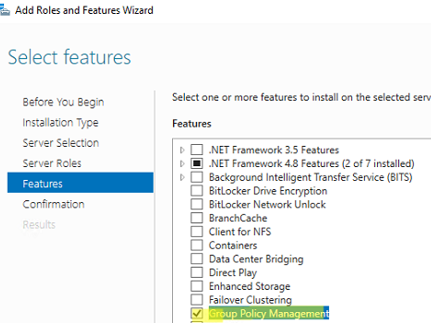
In Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2, you can install the GPO management console through Server Manager: Add Roles and Features -> Features -> check Group Policy Management.
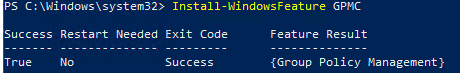
Another way to install the GPMC on a Windows Server is to use the PowerShell Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet:
After installation, check that the Group Policy Management shortcut appears in Administrative Tools in Control Panel. The shortcut refers to the MMC snap-in %SystemRoot%\system32\gpmc.msc .
The GPMC offers various options to manage Group Policies at the AD site, domain, and Organizational Unit levels.
To start the console, type the command:
By default, the console connects to a domain controller with the Primary Domain Controller Emulator (PDC) FSMO role. If you want to connect to a different DC, right-click on the domain name and select Change Domain Controller (it is preferable to use a connection to your logon server).
Expand Forest -> Domain -> Your domain.
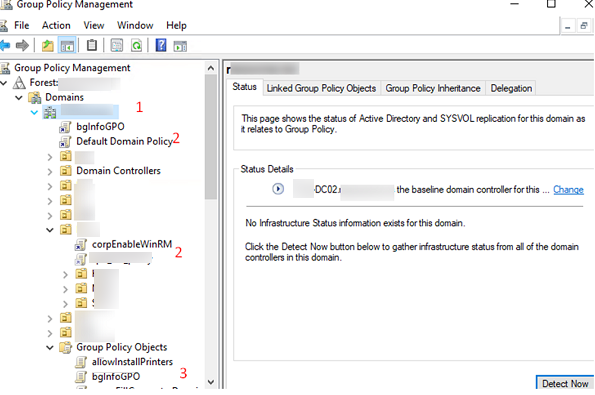
Here in this screenshot, you can see:
Active Directory Group Policies can be assigned to a specific OU, a site, or to the entire domain. GPOs are usually linked to OUs with computers or users.
To create a new GPO and immediately assign it to an OU, right-click on the required container and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.
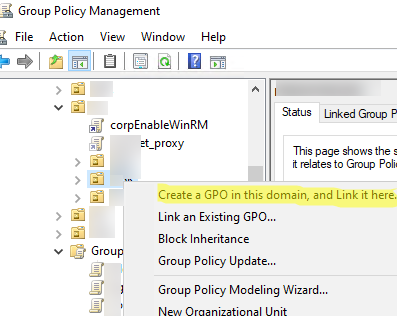
Now specify a name for the GPO:
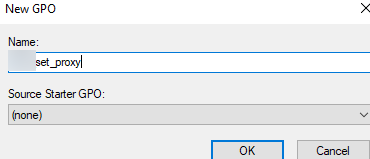
Once that’s done, you’ll see your new GPO assigned to the container (OU) you selected in the GPMC console.

Note that the GPO is enabled ( Link Enabled = True ), which means that its settings apply to all objects within a given OU.
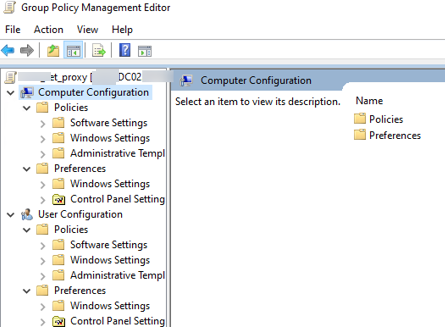
Select Edit to change the GPO settings.
To manage Group Policy settings on a standalone Windows computer, use the local GPO Editor console (gpedit.msc). It allows you to configure Windows settings using single or multiple local policies (MLGPO).
This will open the GPO Editor console similar to the local GPO editor. Note that all GPO settings are divided into two sections:
There are three subsections in each section::
Here are some examples of using GPOs to configure various Windows settings:
There is also a separate Preferences section. It contains an additional set of Group Policy Preferences (GPP) options that you can configure for client devices via the GPO.
With GPP, you can configure user and Windows settings, such as the followingClose the Policy Editor now and go back to the GPMC. Any settings you have configured in the GPO will be applied to the clients the next time the Group Policy settings are updated.
Select your GPO to display its parameters. There are 4 tabs available here:
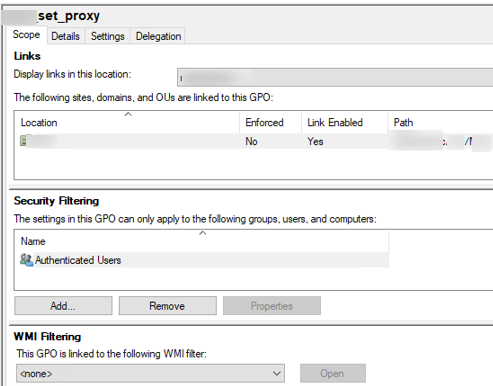
Active Directory stores GPOs as a set of files and folders in the SYSVOL directory, which is replicated between DCs. You can find the directory of a particular GPO by its GUID in the Details tab. Use the following UNC path: \\woshub.com\sysvol\woshub.com\Policies\ .
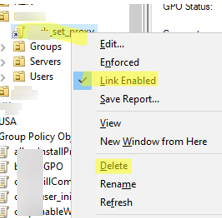
If you no longer want the policy to apply to clients in this OU, you can either remove the link (click Delete, note that the GPO itself will not be deleted) or temporarily disable it ( Link Enabled = False ).
Note that there are already two predefined GPOs in the domain that apply to all the computers and to the domain controllers, respectively:
In most cases, using these GPOs to configure client settings is not recommended. Instead, you should create new policies and assign them at the level of the entire domain or Domain Controllers container.
Other options offered by the Group Policy Management console include:
You may also want to read the article “Why can’t I apply group policy to my computer?” which discusses the basic elements of Active Directory Group Policies, such as
Please look closely at this article to better understand Group Policies and how they work.